M05 Devices and Cabling
Lecture Video
Cabling
Cabling infrastructure is the backbone of the interconnected society. There is no traffic without roads, there is no Internet without cabling.
In Finland there is talk about "road debt", but no talk about "cabling debt". Mainly because most of the telecommunications cabling has been installed by privatized companies (previously owned by the government).
Talking about expected lifecycles of cabling infrastructures
- Copper cabling, decades
- Fiber cabling, centuries
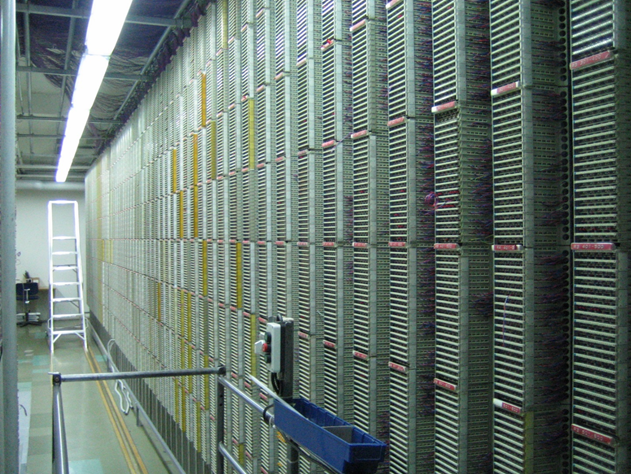
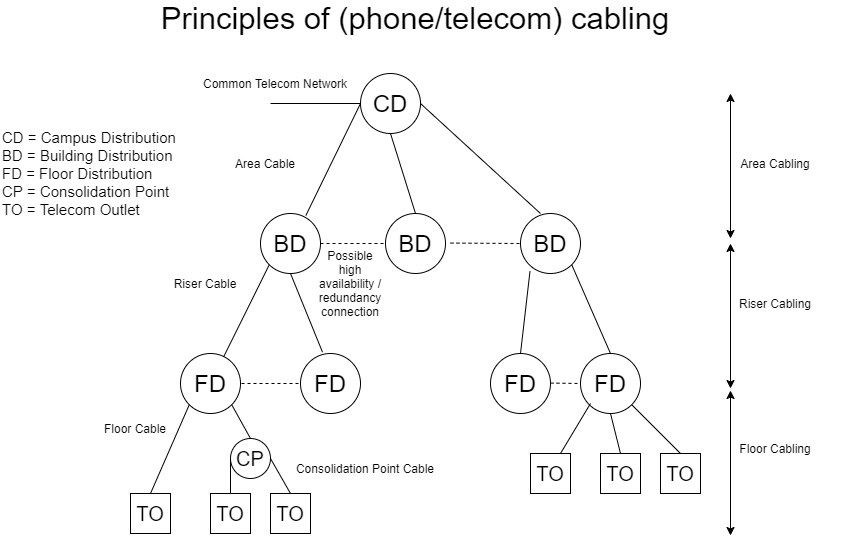
Basic infrastructure of cabling
The figure below represents the basic principles & topologies of the cabling infrastructure in our society. No matter the physical media.
These "distribution facilities" have been established through the decades of wired telephony infrastructures.
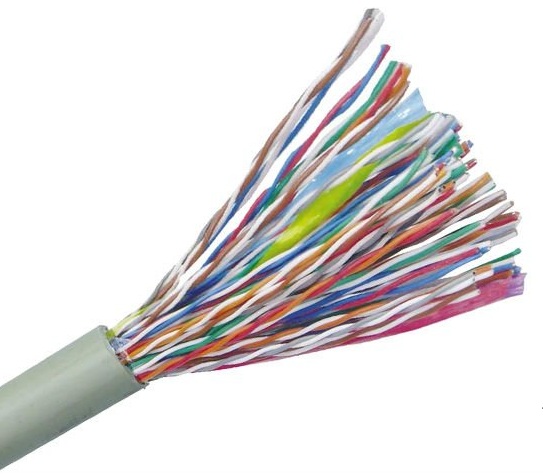
Copper Cabling
Copper cabling is divided into categories (with the exception of coaxial cabling) in the (SFS-)EN 50173 -standard series concerning Generic Cabling Systems.
These categories are gone through here.
| Category | Channel | Class | Maximum speeds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category 3 (phone cabling) | 16 MHz | Class C | below 100Mbit/s, depends on length |
| Category 5 | 100 MHz | Class D | 100Mbit/s |
| Category 5e | 100 MHz | Class D | 1Gbit/s |
| Category 6 | 250 MHz | Class E | 1Gbit/s |
| Category 6A | 500 MHz | Class EA | 1Gbit/s |
| Category 7 | 600 MHz | Class F | 10Gbit/s |
| Category 8.1 | 2000 MHz | Class I | Up and coming standards for 25Gbit/s / 40Gbit/s |
| Category 8.2 | 2000 MHz | Class II | Up and coming standards for 25Gbit/s / 40Gbit/s |
Twisted pair cables reduce electromagnetic interference (called noise)
Physics course will teach you about eletromagnetic waves produced by the transmission of current. And how those waves are received by nearby cables.
Category - 3 (CAT3)
Range: depends on technology
- 5 kilometers for Plain Old Telephone System (POTS)
- 5 kilometers for ADSL
- 2 kilometers for ADSL full-rate
- hundreds of meters for VDSL
Adapters
RJ11 - male adapters, connection cable
Phone adapter - with RJ11 female adapter
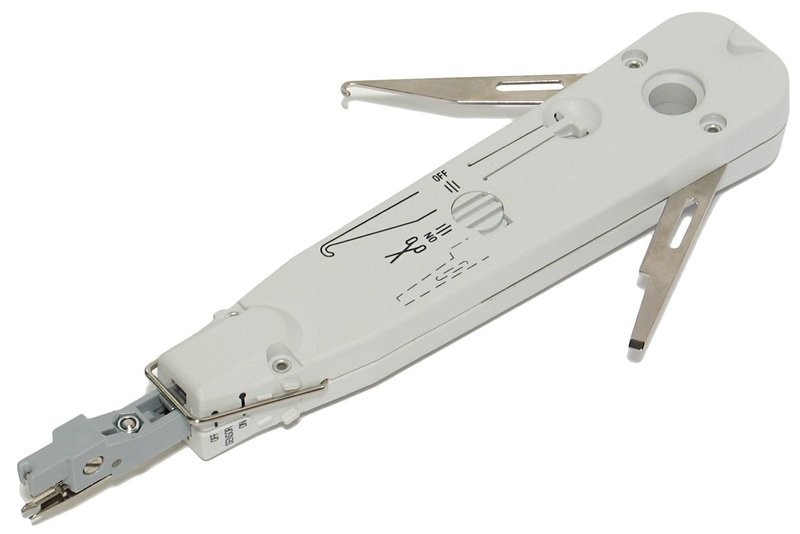
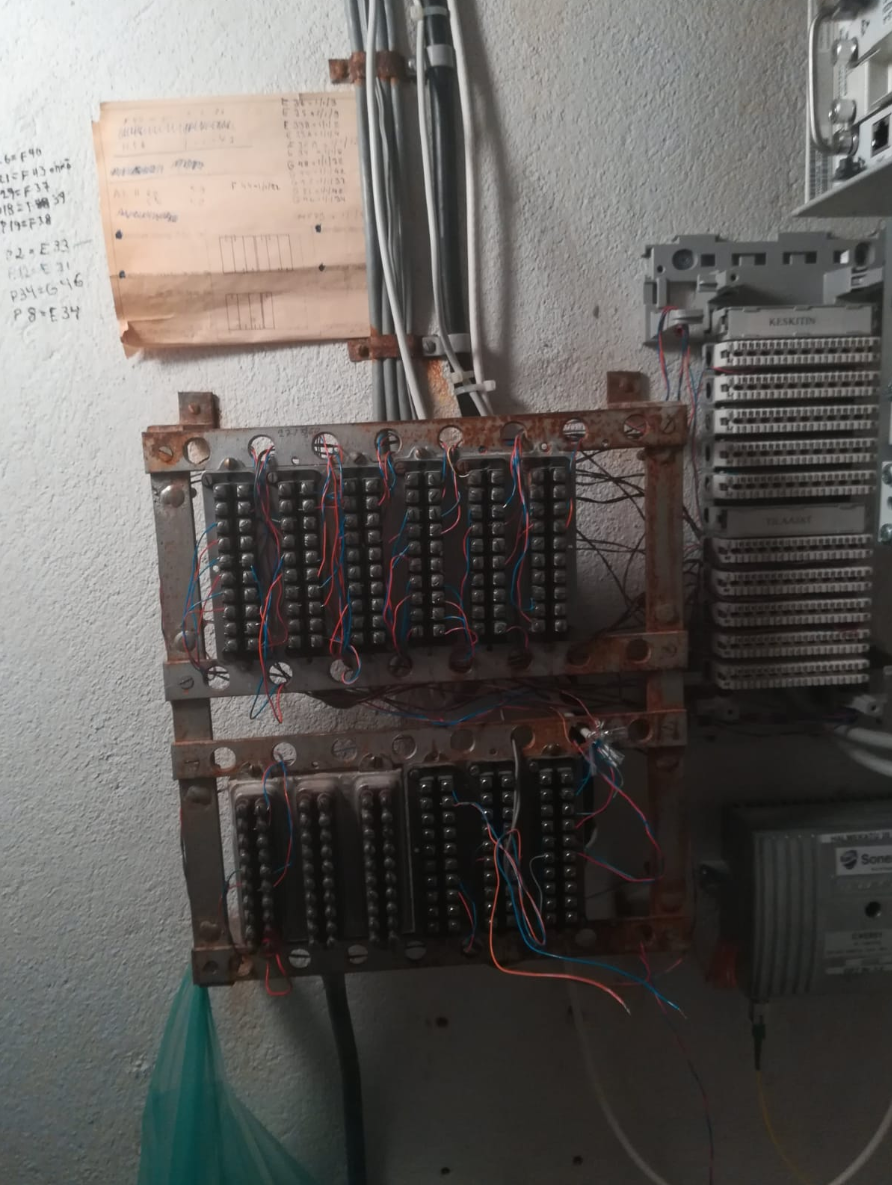
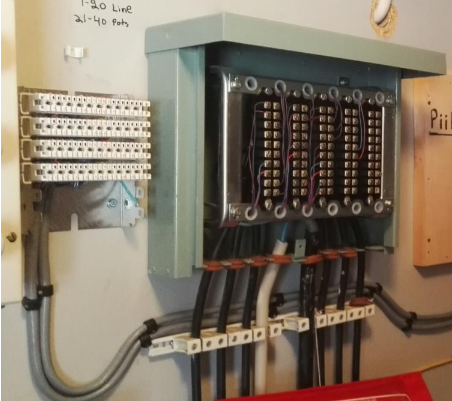
Installation
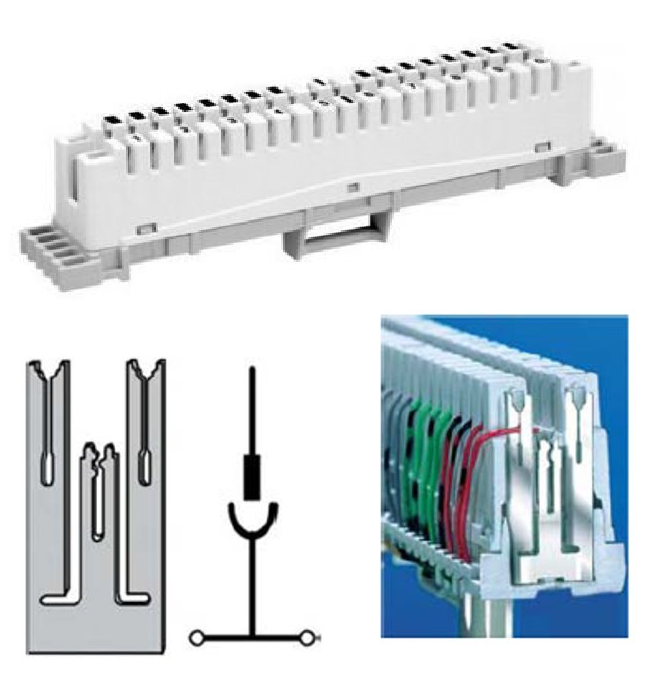
Typically installed on Krone LSA-PLUS connectors.
The wires are connected with use of a special tool:
Category - 5 through 7 (CAT5 - CAT7)
Range: Typically 100 meters
- 10 meters for tail cabling
- 90 meters for ceiling/wall cabling
Types
| ISO/IEC 11801 designation[A] | Cable shielding | Pair shielding |
|---|---|---|
| U/UTP | None | None |
| U/FTP | None | Foil |
| F/UTP | Foil | None |
| S/UTP | Braiding | None |
| SF/UTP | Braiding and Foil | None |
| F/FTP | Foil | Foil |
| S/FTP | Braiding | Foil |
| SF/FTP | Braiding and Foil | Foil |
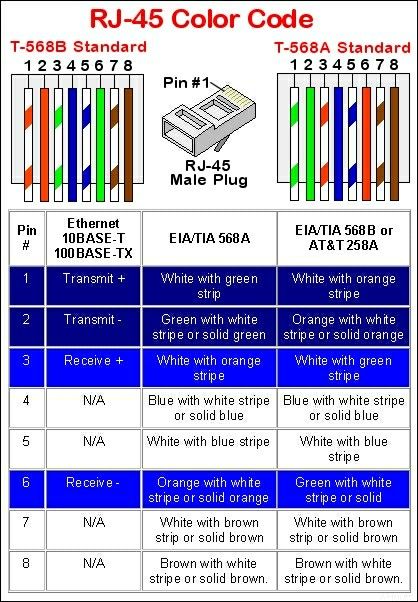
Letter before the slash indicates shielding of the cable. Letter after the slash indicates the shielding of individual pairs. TP is always Twisted Pair.
- U – unshielded
- F – foil shielding
- S – braided shielding (outer layer only)
- TP – twisted pair
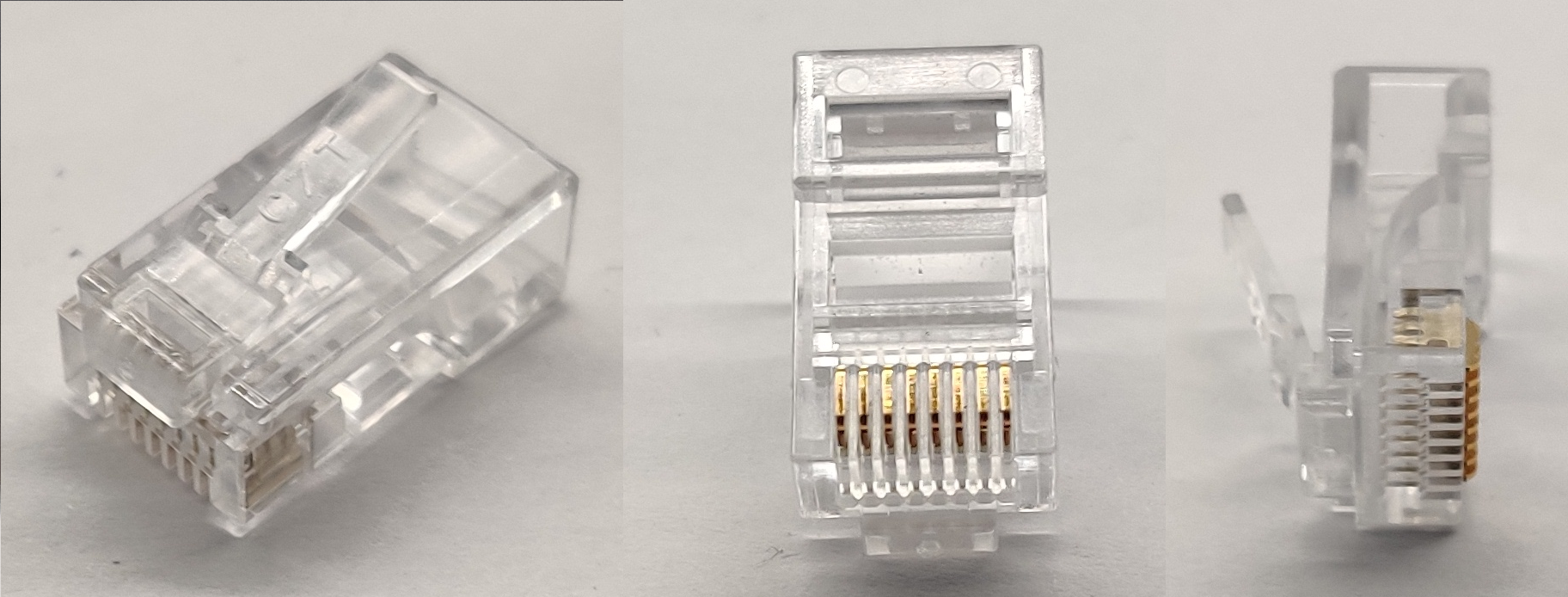
Adapters
RJ45 -connector, one of the most common data network connections today
Installation
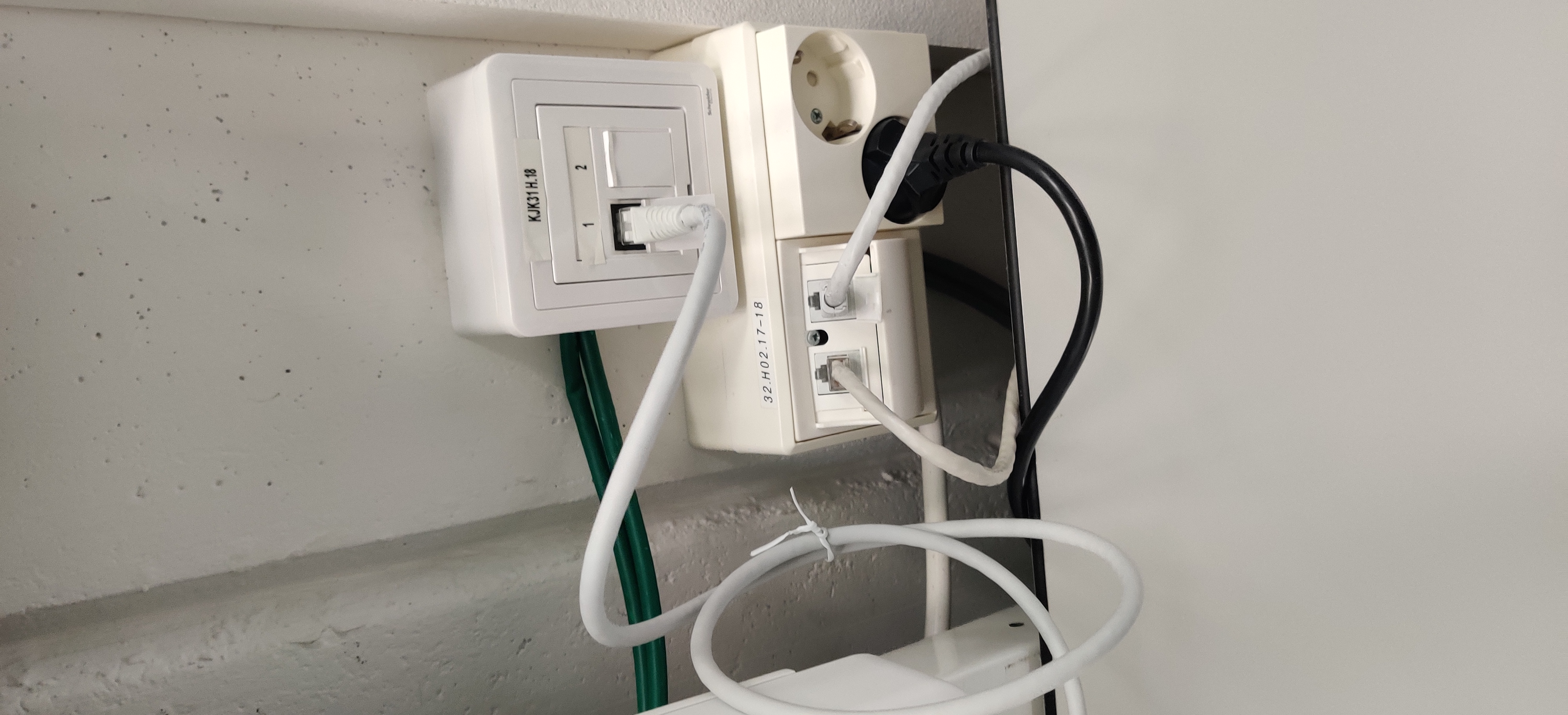
Wall Box for Telecom Outlets in rooms.
Wall Mount Box Cat6 2xRJ45
- Note! Two Telecom outlets with RJ45 cables attached to them on (on both sides)
Typically have Rack -installation in Floor Distribution.
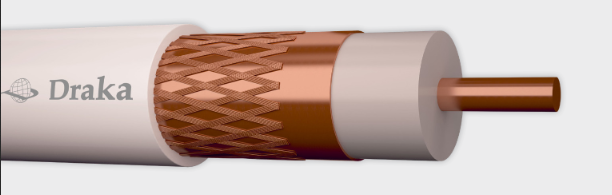
Coaxial Cabling
Coaxial cabling is most often used in Television distribution networks and always in place in Finnish households. Data Networks use Cable Modems (or EuroDOCSIS standard) for IP traffic over these tv networks
Indoor use
Outdoor use
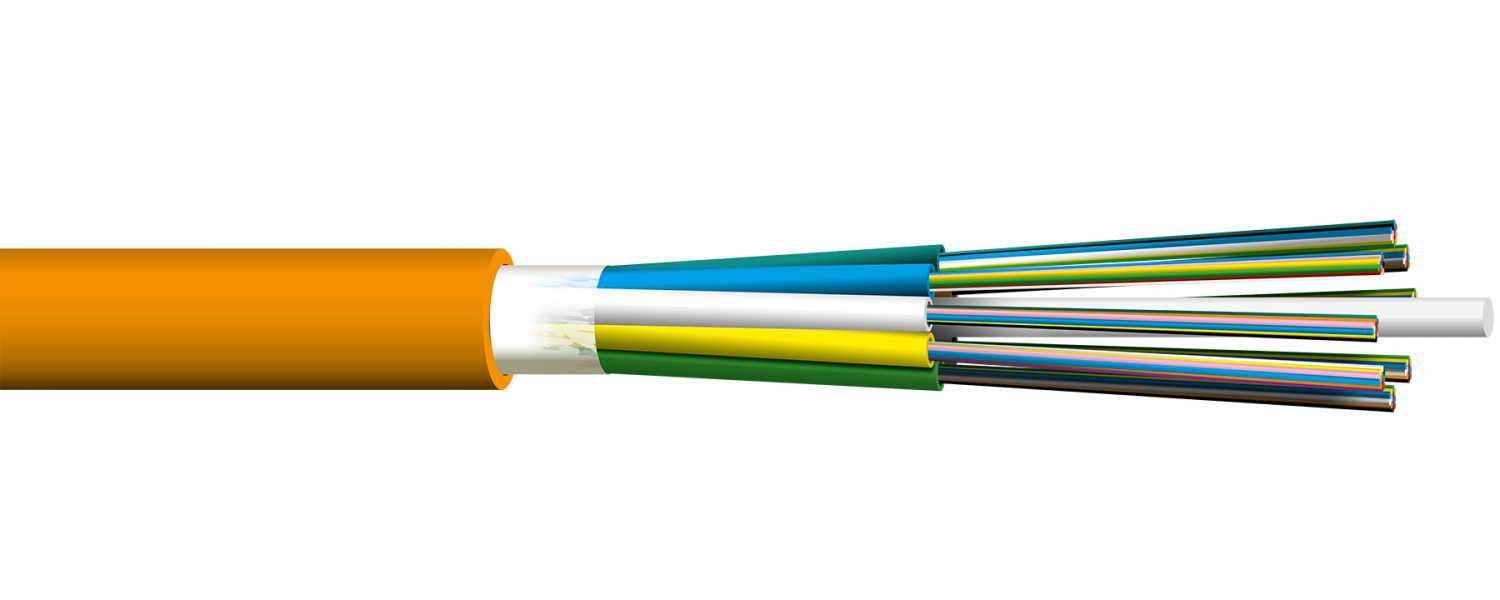
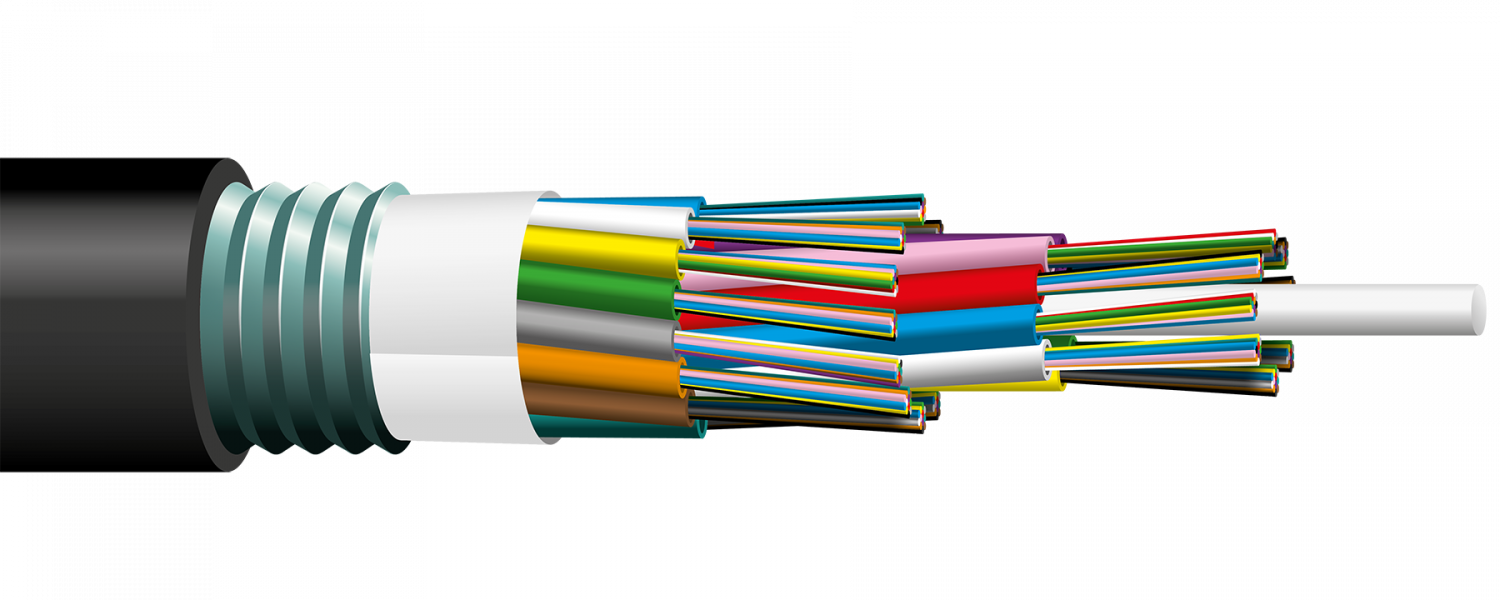
Fiber Cabling
There currently is no replacement for fiber cables in sight. Photons are the fastest way to transmit data and given the wavelengths of fiber cables, the bandwidth limit is in the electronics at the end of fiber cables. Rather than the cable itself.
Fiber cabling is dangerous
Do not operate/install unless you know how to protect yourself.
Do not point them towards your eyes!
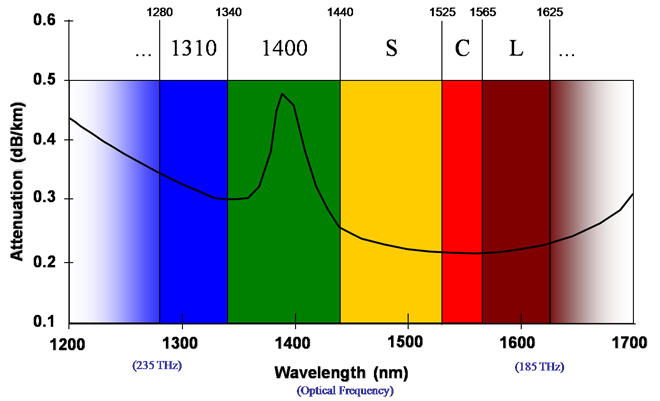
Single Mode Fiber - SMF
Single Mode Fibers send their transmission in 1200nm - 1600nm wavelengths. Most commonly 1310 nm, but other wavelengths do exist in transmission through wavelength division multiplexing techniques.
These fibers have lengths from 10 to 80 km on typical hardware designed on land. (Thousands of kilometers when seacables and electronics are discussed.)
Multimode Fiber - MMF
Multimode fibers exist because they are chepear to produce. They are a typically a within building solution, but are less frequently installed.
Multimode uses the wavelength of 550nm
Wavelengths? Electromagnetic spectrums? What?
Adapters
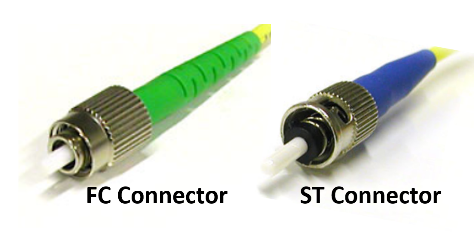
Adapters for fibers are of different sizes and formats based on usage.
LC -adapter - Maybe the most common attachment in devices.
SC -adapter - Maybe the most common attachment in patch panels.
Types
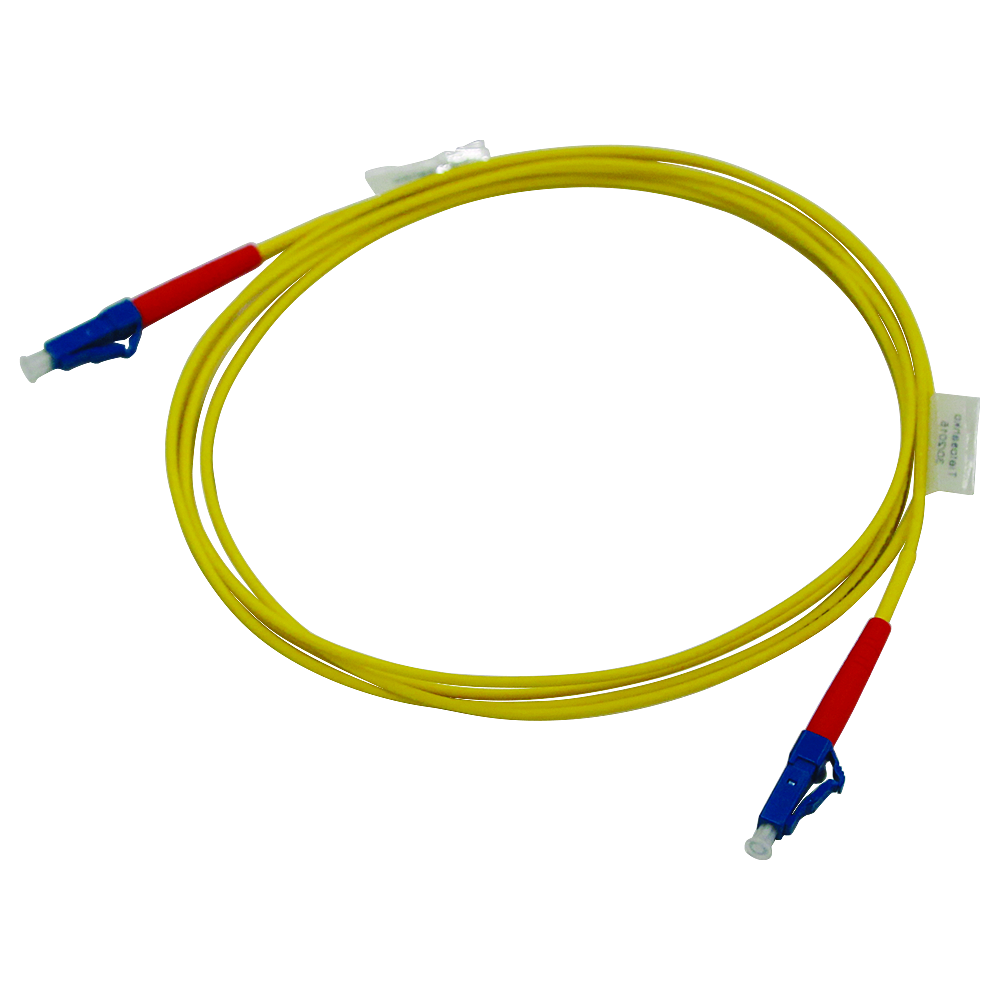
Cross-connection / Patch Cables
FMS OS2 OS2 LC/LC/1/2m
So a cross-connection cable, with LC adapters on both ends, 1 fiber and 2 meters of length
- Source Onninen
Indoor cables
Outdoor cables
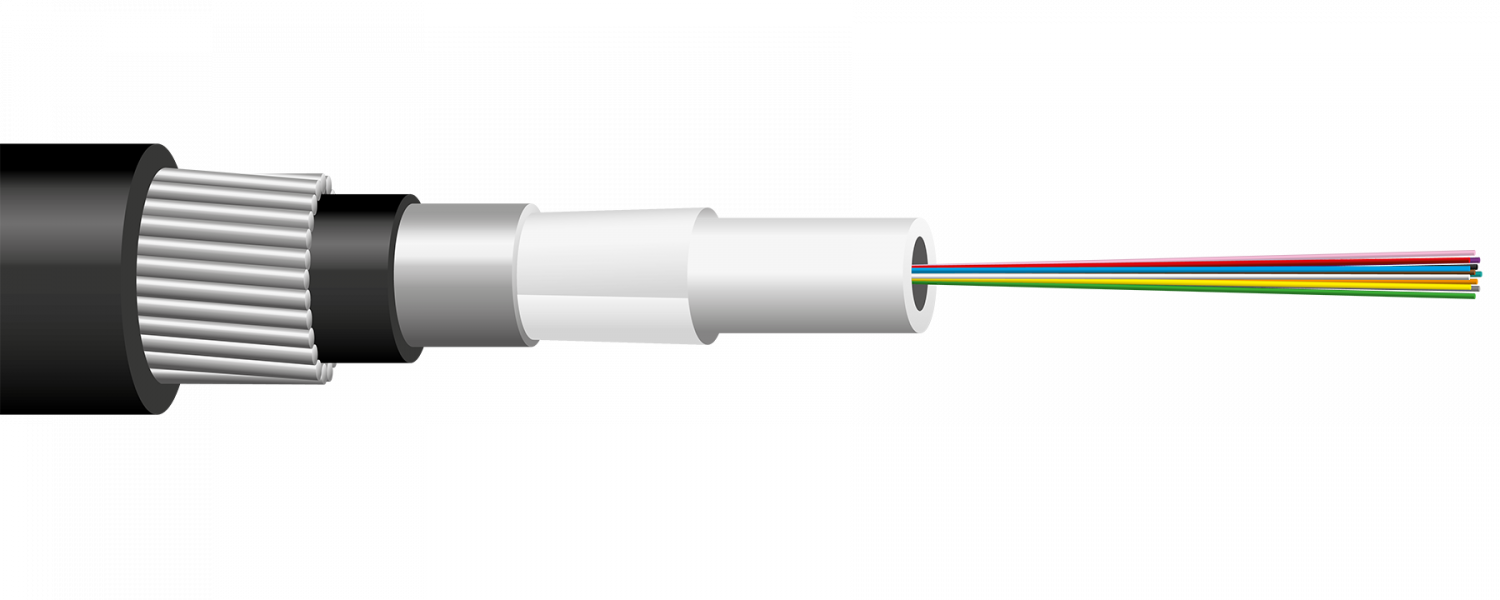
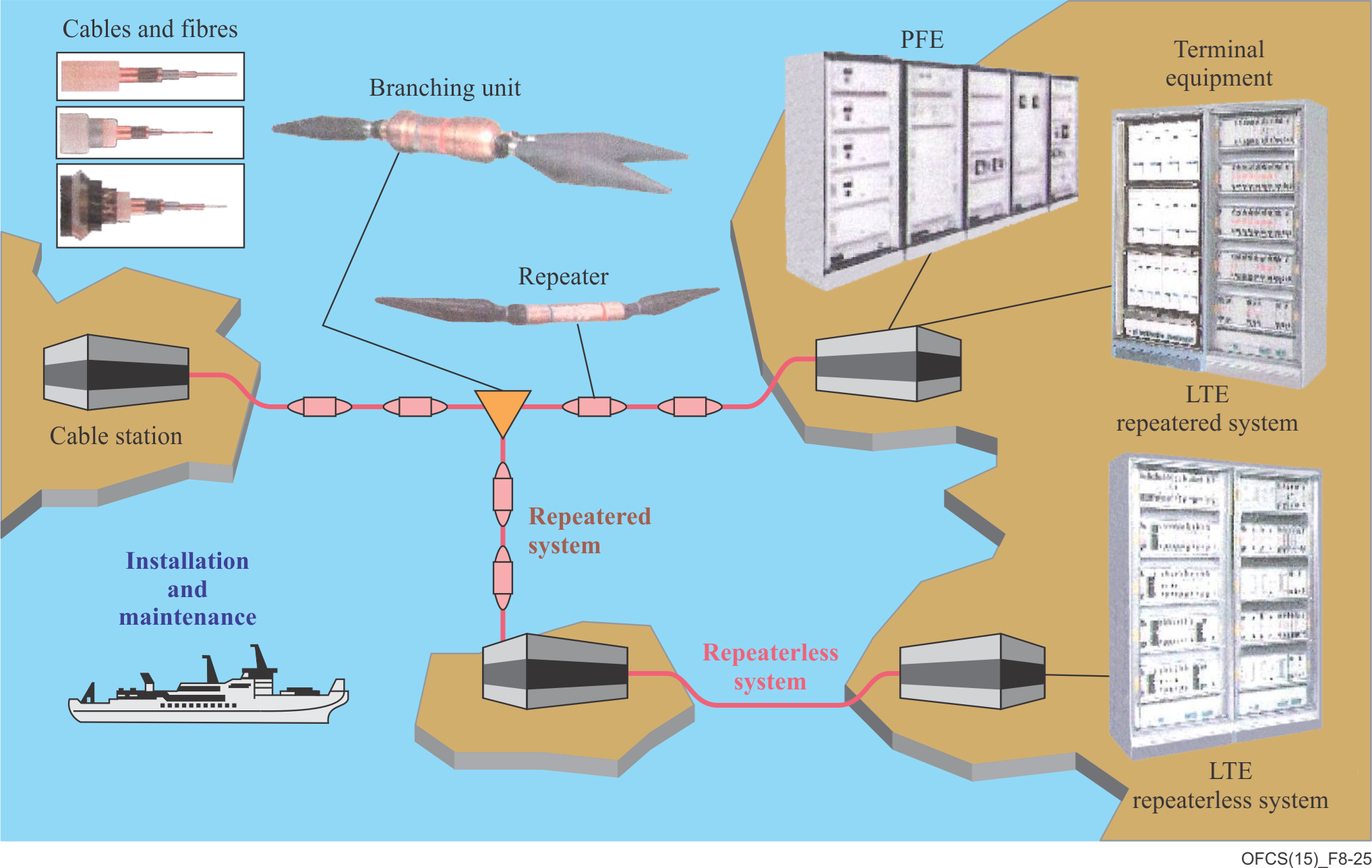
Seacables
Seacable FYOHBMP 1,6MW
"1.6mm^2 steel wire armoured cable for sub-water installations. Can withold either 12, 24, 48 or 96 fibers."
- Source Nestor cables
More on Submarine cables?
"Starting from the first transatlantic optical cable system with a single-channel per fibre pair at 280 Mbit/s in 1988, the evolution of the technology has arrived at DWDM systems on transoceanic links with a capacity of 128 × 10 Gbit/s per fibre pair."
- Source ITU-T
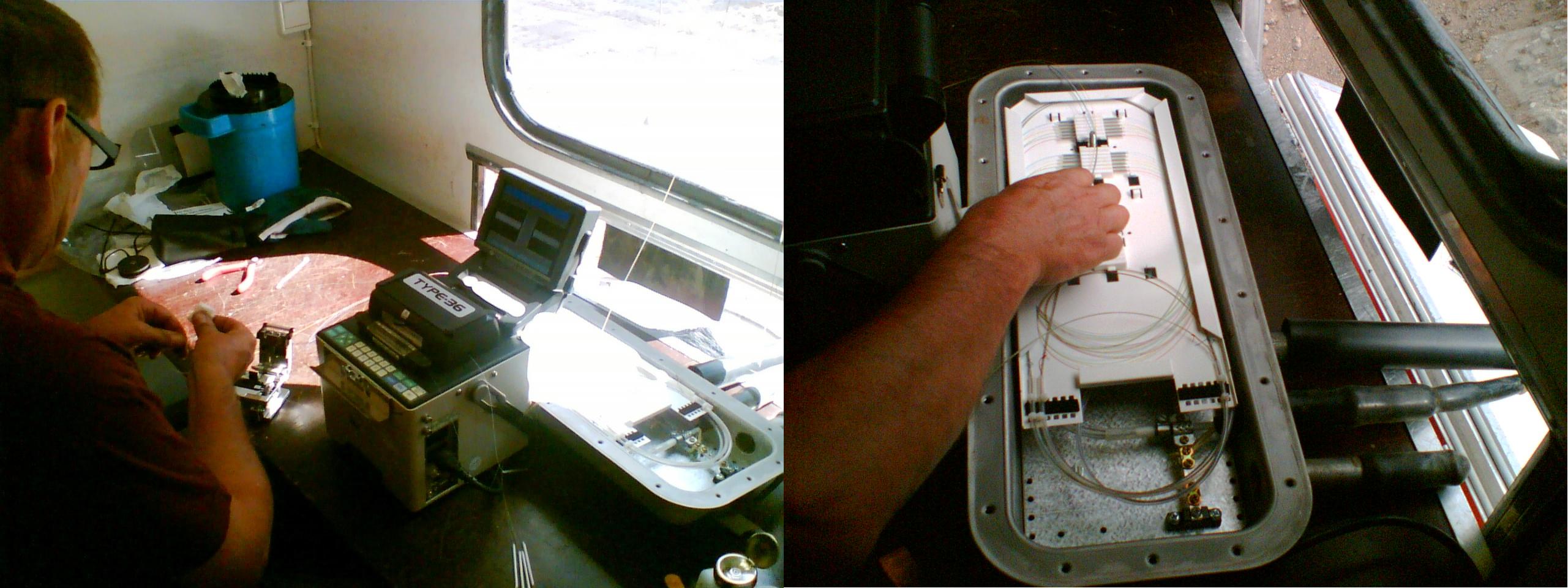
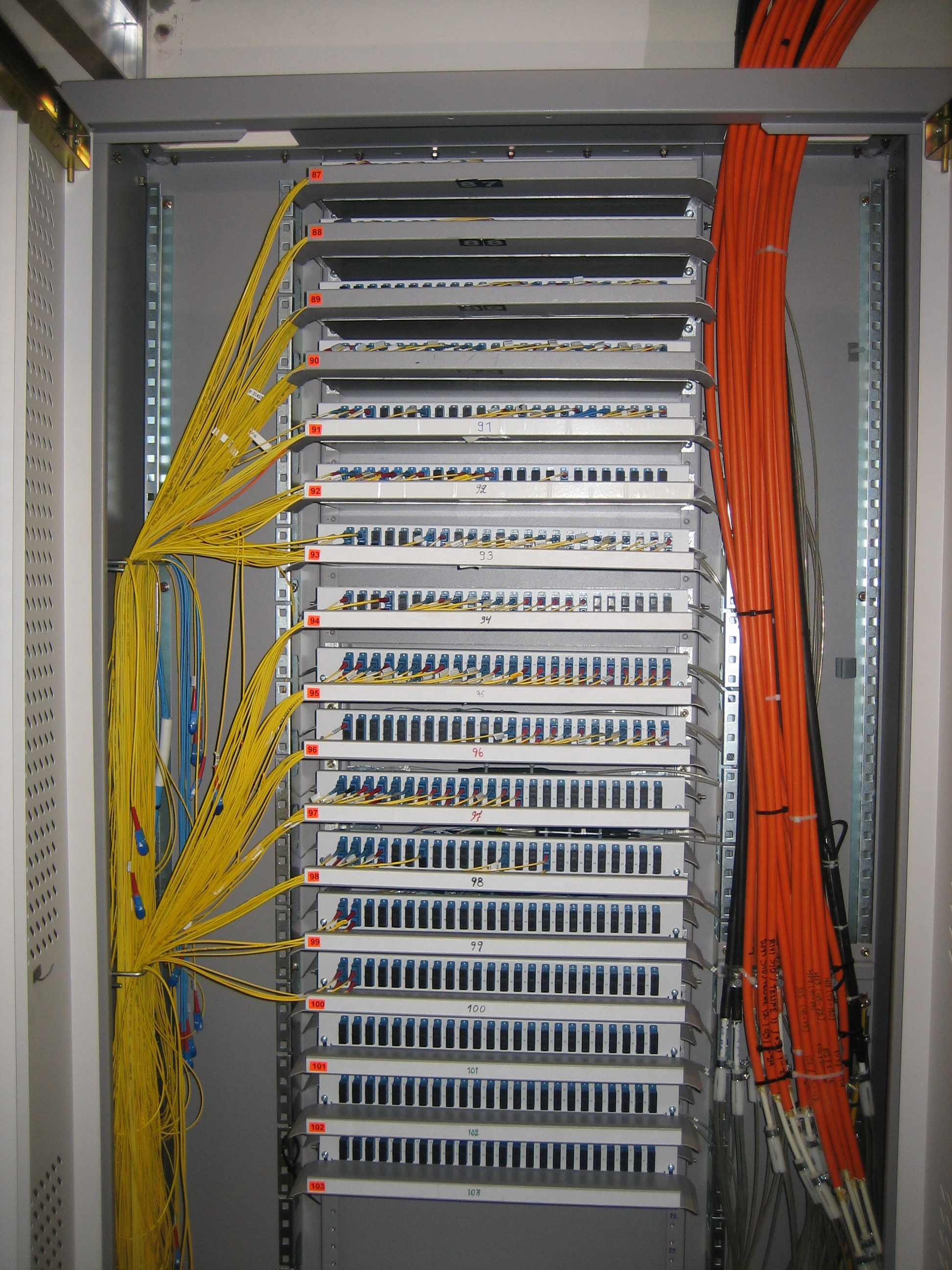
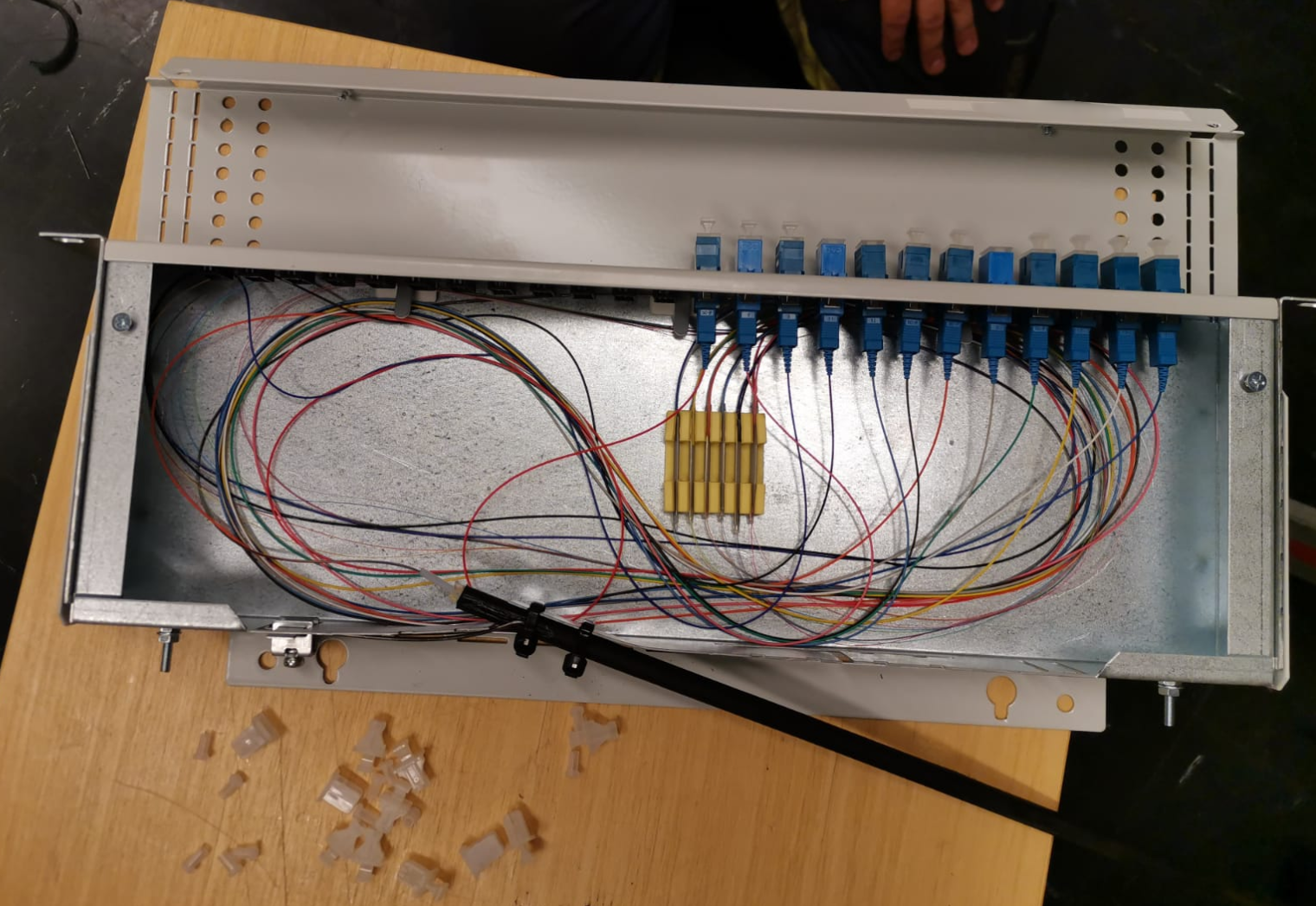
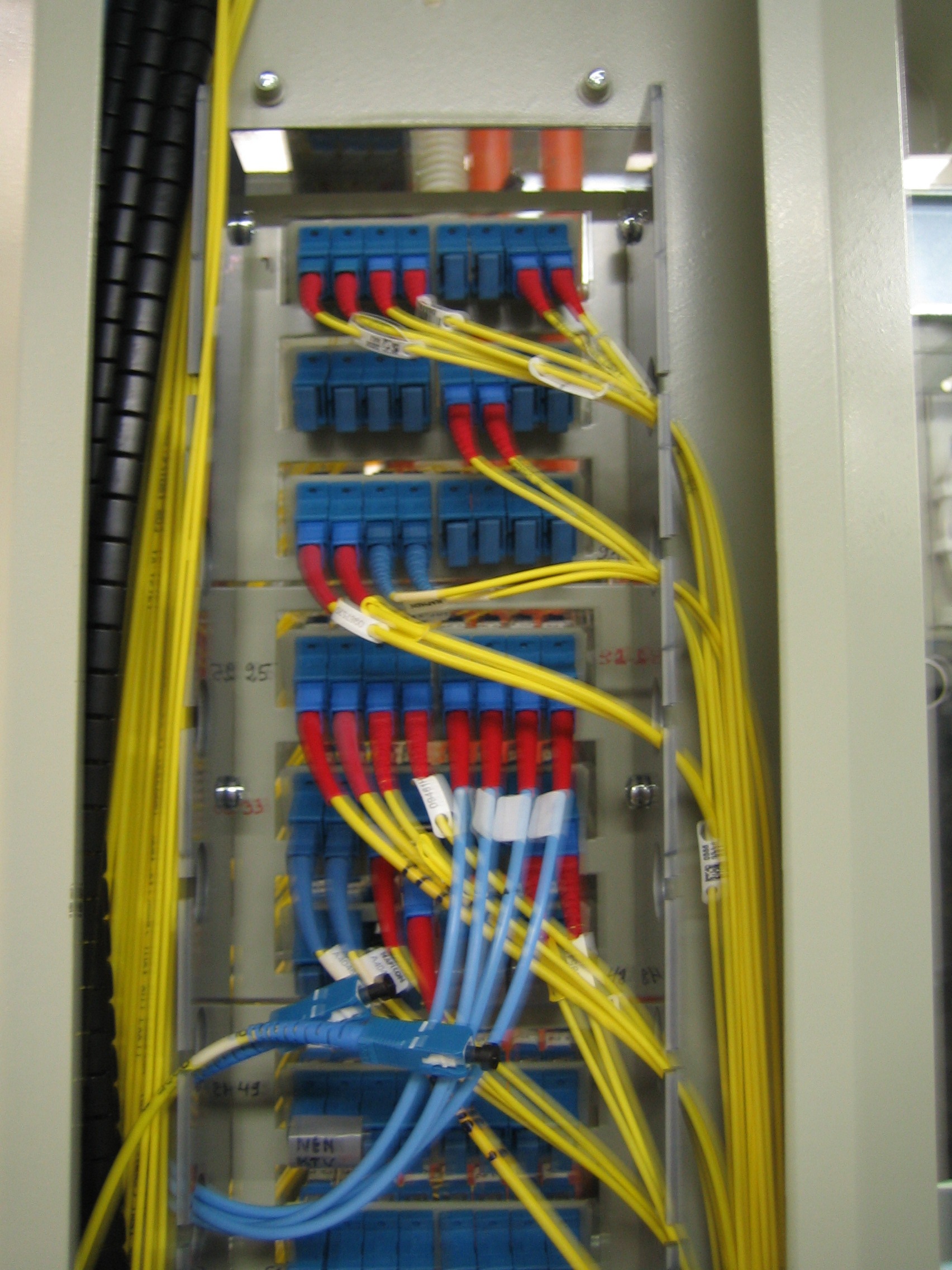
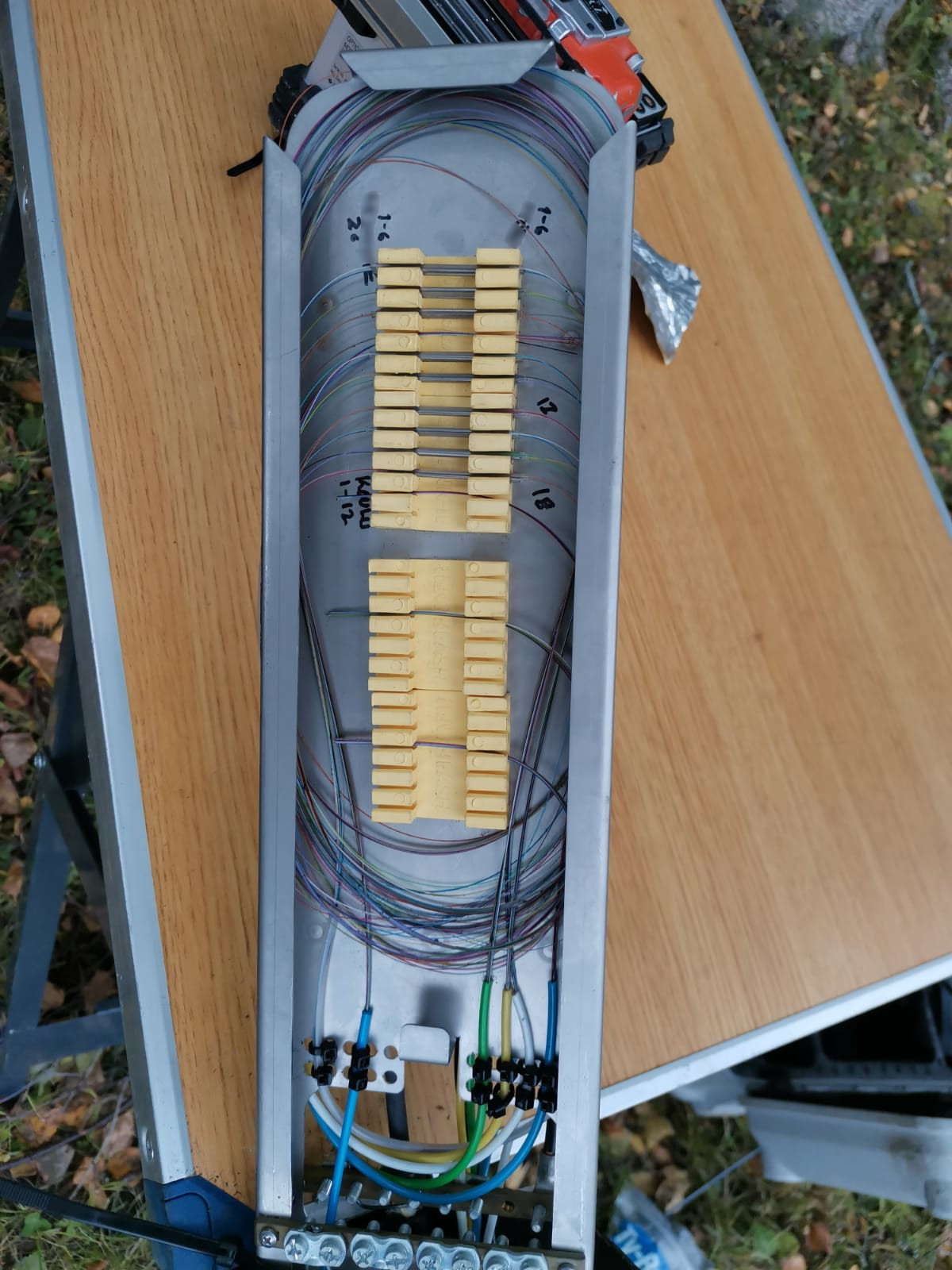
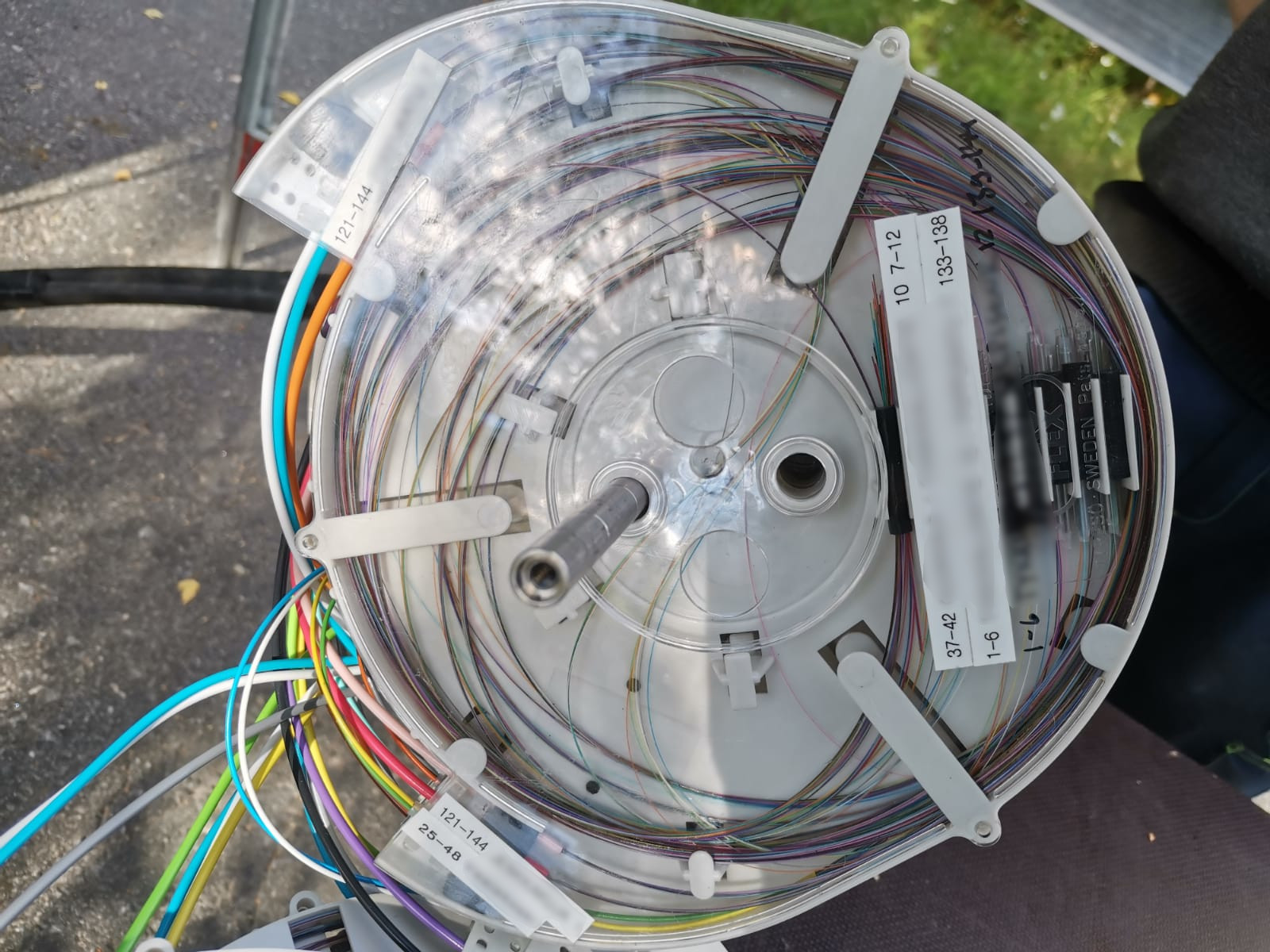
Installation
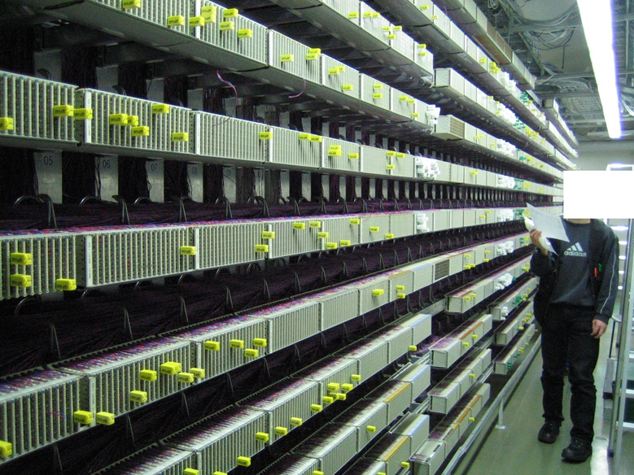
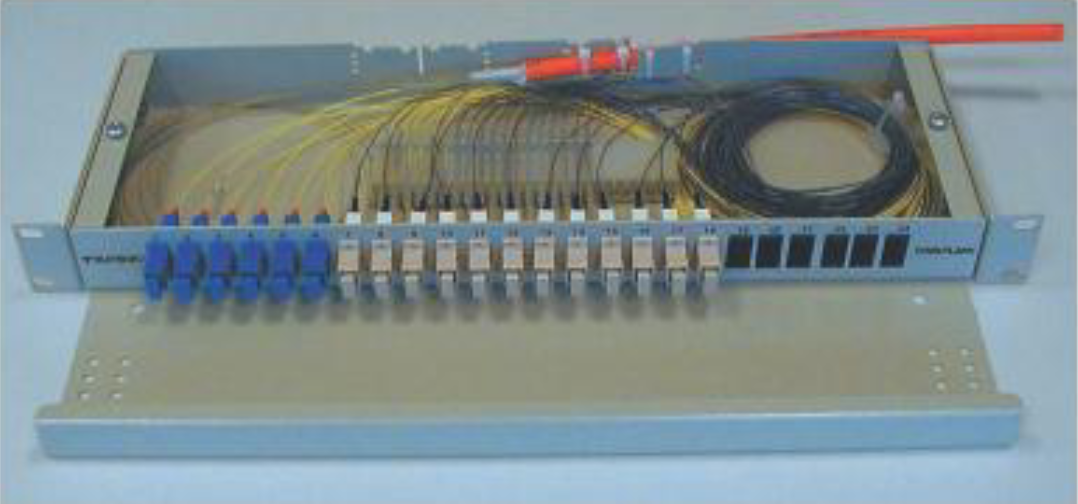
Typically a 24 fiber patch panel installation to 19" racks.
Fiber welding on the left and a ground installable extension box.
Devices
Data Network devices are robust hardware, but also have an technical lifecycle.
Approximate average lifecycles (depending on use) for different devices:
- Mobile phones, 2 years
- Computers, 3 - 6 years
- Laptops, 2 - 5 years
- Network devices, 6 -10 years
Of course these are just estimates of average life cycles, but devices have to be renew'd from time to time. Either to have replacement parts or get new technology into use for the organization (e.g. Software-Defined Networking).
We start our journey from old to new.
Hub / Repeater
Be it electric current in wires or photons in fiber connections, signals attenuate while traversing through the cabling.
This means that repeaters are needed to enhance the transmission. Repeater's have been present a long time, that is why the term 'broken-phone' is familiar even as a kids game.
Ethernet repeater - fibre cabling
"Submarine fiber has attenuation. Repeaters are used for optical signal amplification. Repeaters are placed every 60km to 70km."
- Source: www.submarinenetworks.com
Hubs and repeaters are excellent for investigating network traffic through packet sniffers. And this introduces us to...
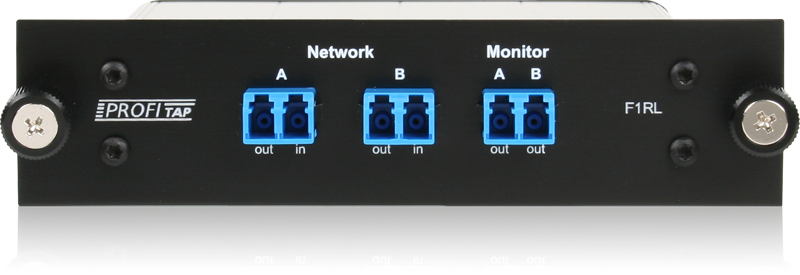
TAP / Network Sniffer
It is illegal to interfere & read communications in Finland!
5 § Vaitiolovelvollisuus ja hyväksikäyttökielto
Se, joka on ottanut vastaan tai muutoin saanut tiedon luottamuksellisesta viestistä tai tunnistamistiedosta, jota ei ole hänelle tarkoitettu, ei saa ilman viestinnän osapuolen suostumusta ilmaista tai käyttää hyväksi viestin sisältöä, tunnistamistietoa tai tietoa viestin olemassaolosta, ellei laissa toisin säädetä.
- https://www.finlex.fi/fi/laki/alkup/2004/20040516
Because we can repeat signals, we can also do multiport repeaters where, - One port for incoming transmission - One port for outgoing (amplified) transmission - One port for "tapping" into the transmission (read: eavesdrop)
As mentioned, these are great for learning networking, but at wrong places they are also harmful/illegal.
The equipment still exists.
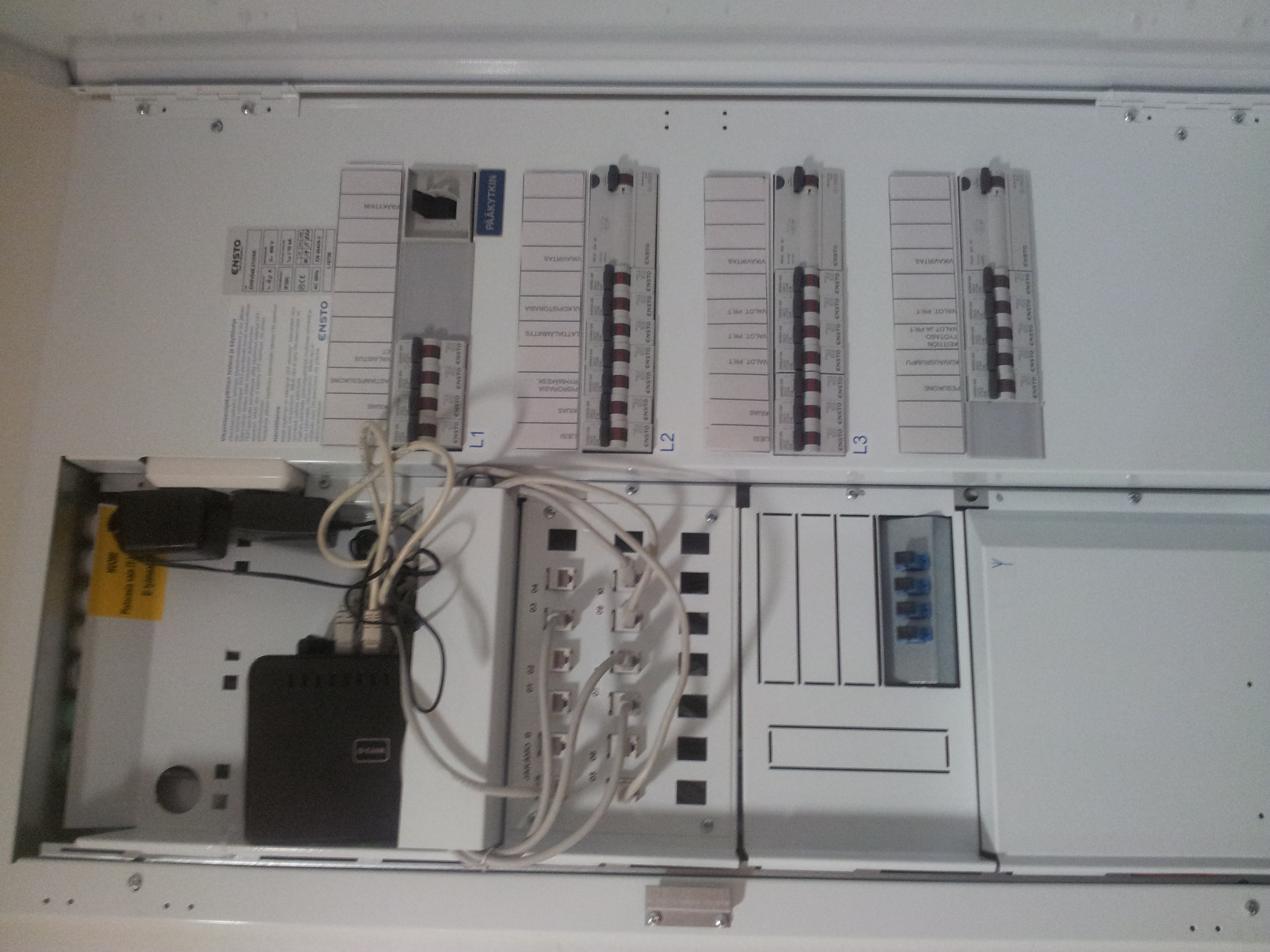
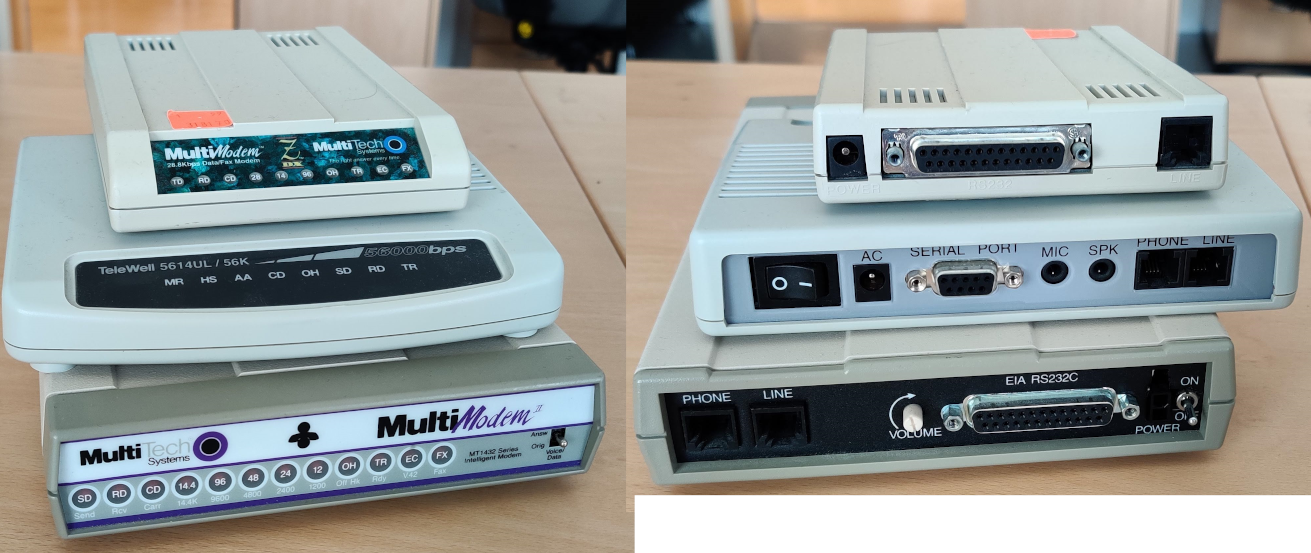
Modem
Communication cables have modulations to improve efficiency in transmission (bandwidth, signal to noise ratio, electromagnetic spectrum usage). This means that there have been a lot of modems throughout the ages, and more are in development.
The kind of modem depends on what kind of electromagnetic spectrum is used and what transmission medium is at hand (air, copper cable, fiber cabling).
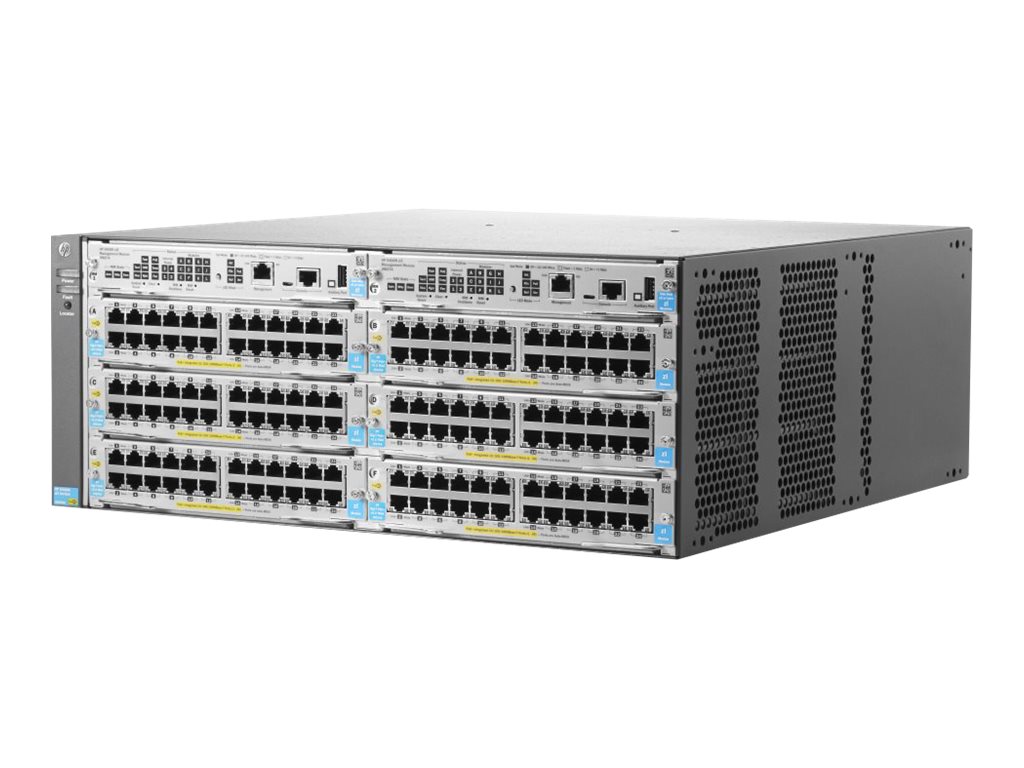
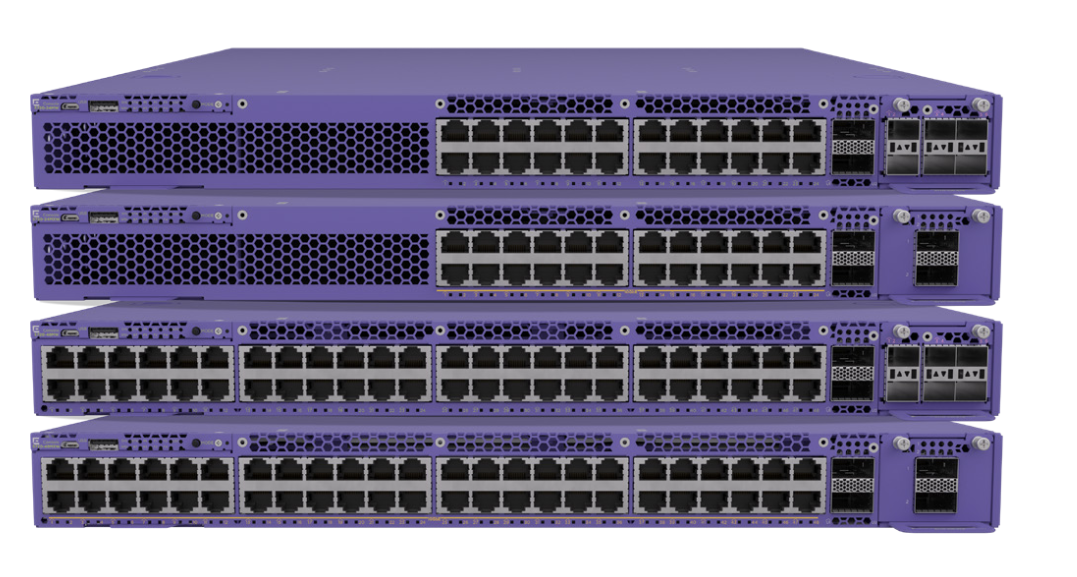
Switch
Switches are the most common network equipment in buildings equipped with physical copper/fiber ethernet cabling.
Physical Switches
Switches span across modular to fixed size switches. From small needs to bigger enterprise needs.
Storey buildings in Finland
Almost all households have a switch in their Mains room (fi: Sähköpääkeskus) that is operated by an ISP.
Industrial buildings in Finland
Also different industry buildings (such as IT-Dynamo) has switches in their cabling racks.
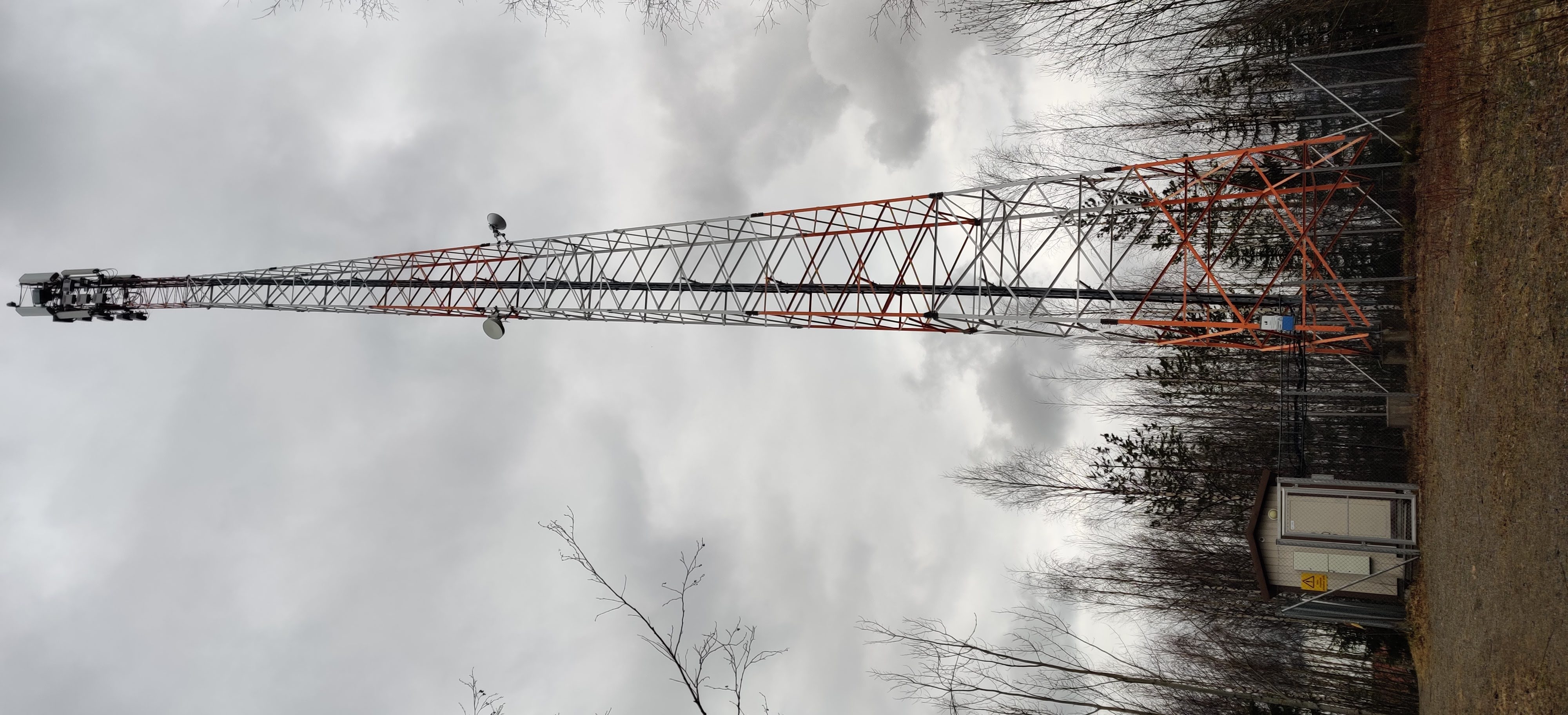
Wireless Basestations
Most of our communications at the network edge are moving towards wireless technologies such as 4G / 5G or WLAN. This still means that the wireless section of the transmission is just
- WLAN, hundreds of meters
- 4G / 5G, kilometers
These distances are of course adjusted by the used frequencies, directional antennae, line of sight and weather conditions. All of them affect the spreading of the electromagnetic spectrum. And thus cause instability for user connections.
Quite often the most commonly recognized device by consumers is the WLAN / Modem / Router / Firewall box. This thing is used by most consumers and thus is really competetive market. Thus the box has all the functionalities crammed into one, but with consumer-grade life-cycle, manageability and replaceability.
Router
Commercial grade routers are the backbone of the Internet. Given the term they connect to the Internet with multiple different WAN options keeping sites alive through dynamic routing.
Firewalls
Firewalls are typically L3 routers, but with enhanced traffic inspection capability. They have the ability to enforce Firewall policies which;
- Deny
- Permit
- Reject, deny and send a TCP RST or an ICMP port unreachable message to the source host
- Encrypt/decrypt (direct into a VPN)
- Authenticate (e.g. enforce web portal authentication)
- Prioritize (Input Quality of Service markings such as TOS or DSCP)
- Schedule (insert the traffic into a traffic queue for a scheduler to handle)
- Filter (scrap stuff out from the packet)
- and monitor (log the traffic)
All of these give the network administrator capability to enforce security into a network. They are typically stated as perimeter (cybersecurity) defence, but it is really a matter of planning and placement of firewalls.
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) & Firepower Series
- Source Firepower series, Cisco
- Source ASA series, Cisco
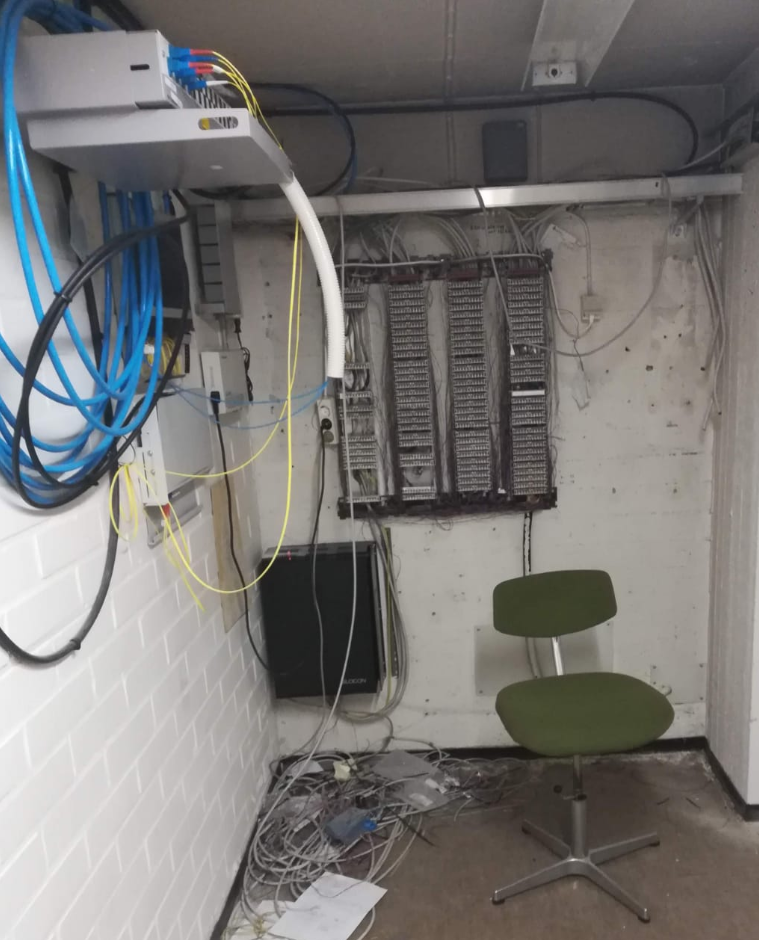
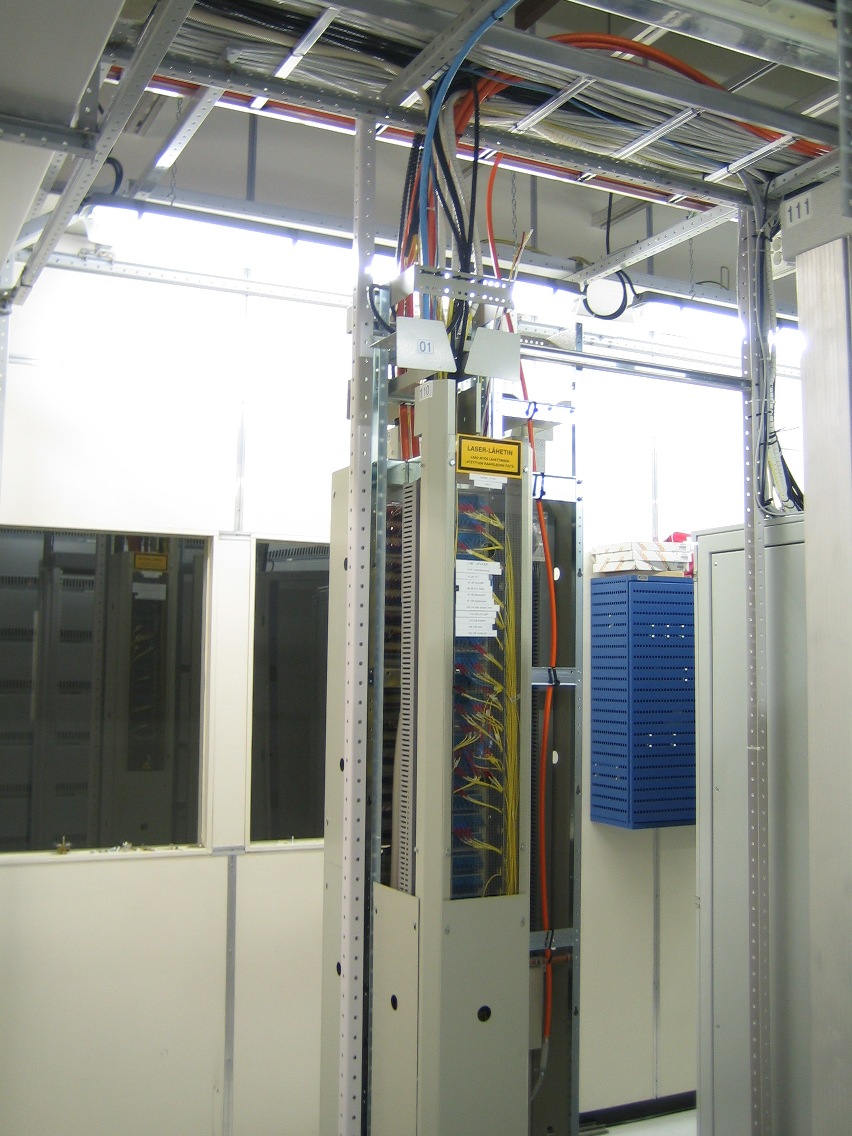
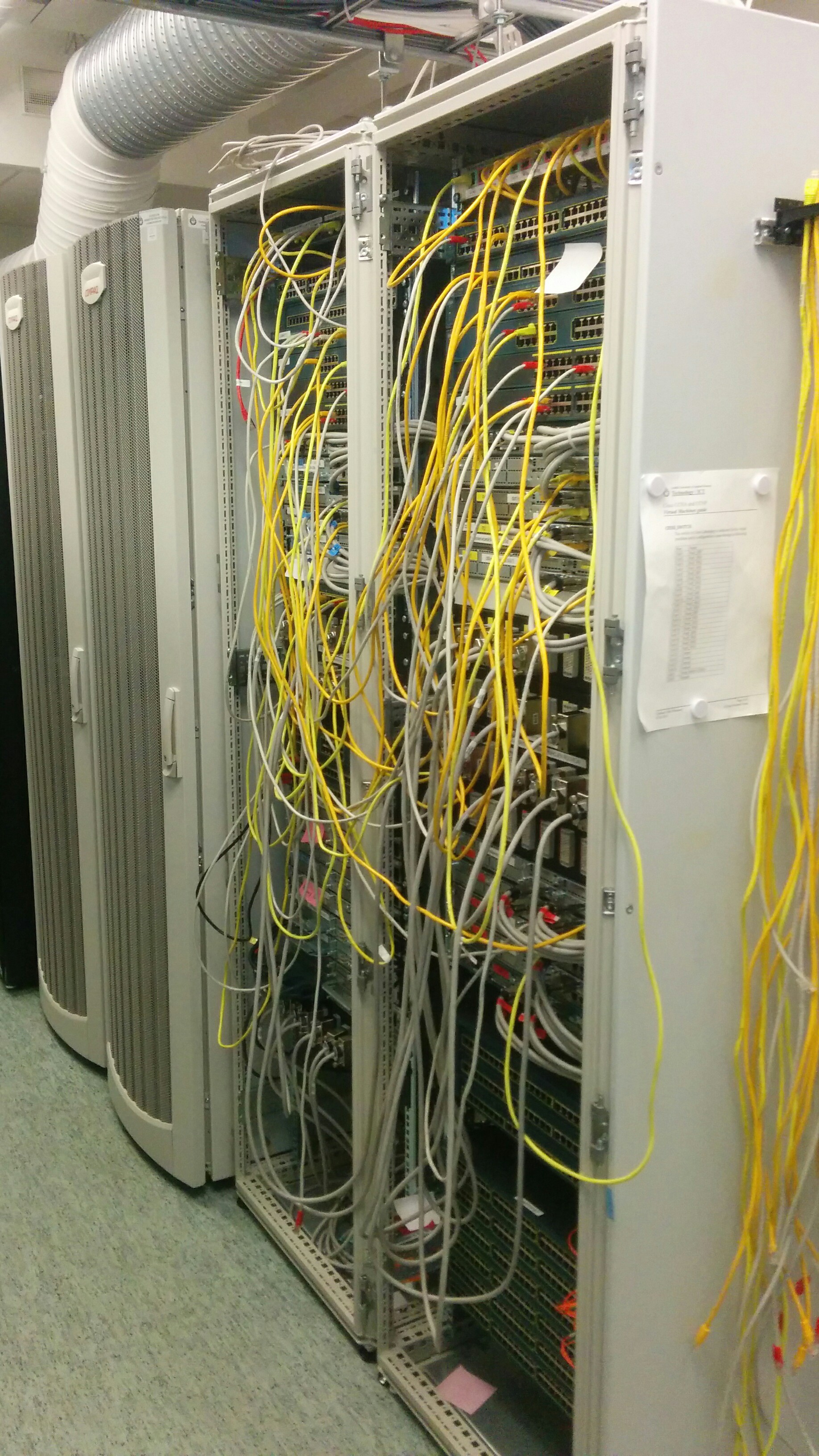
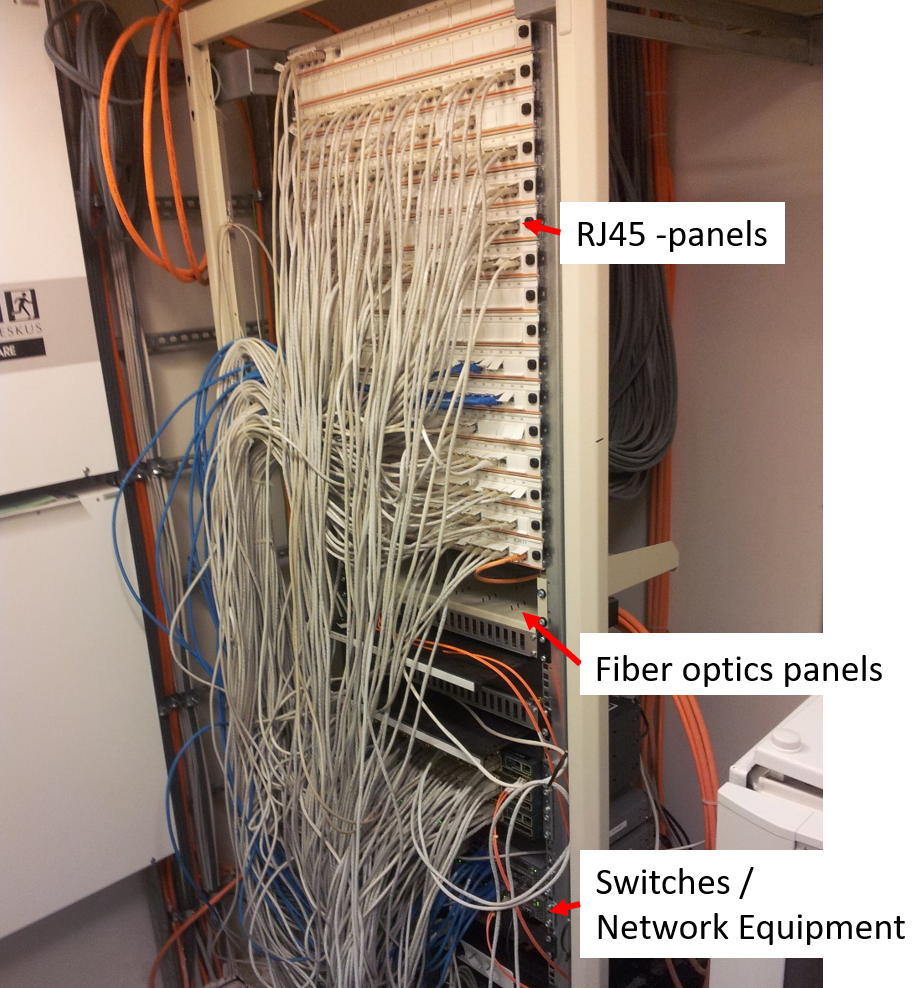
Rack's / Device Cabinets
- Floor distribution
- Building distribution
- or even a Data Center in itself
These environments need a sturdy installation cabinet, usually called racks. The type of rack depends on usage/purpose.
Network devices are required to be behind locks by the Finnish Transport and Communications Agency
Generally on Rack Unit(s)
The Rack is divided into Rack Units (RU's or typically just "U's", e.g. 9U).
The Rack Units in Europe are typically 19 inches in width (482,6mm)
Height of 1 Rack Unit = 1,75 inches = 44,45mm
The problem of cabinets is
- Cooling
- Network Devices & Servers produce heat
- Cabling
- Quite often the devices need a Data Network and electricity
Wall Cabinets
Floor Cabinets
Full size Cabinets
Depth 600, Width 600 (600x600)
This cabinet width allows more cabinets into a room, but with less cabling & cooling space.
Depth 600, Width 800 (600x800)
Wider cabinet (800) gives room for cabling and airflow on the sides
Depth 800, Width 800 (800x800)
Typically the biggest cabinet size. Allows cabling paths and air flows to travel within the cabinet.
Additional installation hardware
Electricity
Shelves
Completely extra materials
These videos will probably be subtitled in english... at some point or another
Keski-Suomen Sairaanhoitopiiri - Sairaala Nova - ICT -luento, JAMK / IT-instituutissa 26.11.2019
Video starts with the data network -related section:
Microsoft Stream (sharepoint) video
Ramboll - Sairaala Nova - sähkösuunnittelu (tietoliikenne) uuteen sarairaalaan, JAMK / IT-instituutissa 10.12.2019
Video starts with the cabling documentation ...
Microsoft Stream (sharepoint) video
Continue to the Exercises
Self-reflect the material with a small quiz?
![]() Data Networks Quiz - M05 Devices and Cabling
Data Networks Quiz - M05 Devices and Cabling
Back to the Schedule?
License
This course and its materials are written by Karo Saharinen and licenced by Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) license.